What is HTTP/2?(什么是 HTTP/2?)
Before diving straight into the topic, let’s first look at some of the HTTP/2 terminologies used frequently.
在深入讨论之前,让我们先看下经常使用的一些 HTTP/2 的术语。
Stream: An established bidirectional connection which may carry one or more messages
Message: A complete sequence of frames that represents a request or response message
Frame: The smallest unit of communication in HTTP/2. Each frame contains a frame header which could identify the stream to which the frame belongs.
h2: Short term for HTTP/2
流: 已建立的双向连接,可以携带一个或多个消息
消息: 表示请求或响应消息的完整帧序列
帧: HTTP/2 中最小的通信单位。 每个帧包含一个帧头,它可以识别帧所属的流。
h2: HTTP/2 的短期
Note: It was originally named as HTTP/2.0 but later “.0” part was dropped because it has caused some confusions with HTTP/1.x. So we no longer use HTTP/2.0, it’s HTTP/2 or h2 for short 😊
注意:
它最初被命名为 HTTP/2.0,但后来“.0”部分被删除,因为它引起了 HTTP/1.x 的一些混淆。 所以我们不再使用 HTTP/2.0,简而言之是 HTTP/2 或 h2
Overview of HTTP/2
HTTP/2 的概念
HTTP/2 is a major revision of the HTTP network protocol which is still being widely used over the World Wide Web. It was developed to overcome some of the drawbacks found in HTTP/1.0 and HTTP/1.1 versions. Overhead of repetitive headers and Head-of-line blocking (HOL blocking — when one request is blocking others from completing) are two such major problems addressed.
HTTP/2 是 HTTP 网络协议的主要修订版,它仍在万维网上广泛使用。 它的开发是为了克服 HTTP/1.0 和 HTTP/1.1 版本中的一些缺点。 重复标题和 行头阻塞 的开销(HOL 阻止 - 当一个请求阻止其他人完成时)是两个这样的主要问题。
HTTP/2 enables more efficient use of network resources, header fields compression, multiple concurrent exchanges on the same connection reducing the latency to a great extent.
HTTP/2 可以更有效地使用网络资源,头字段压缩,同一连接上的多个并发交换,在很大程度上减少了延迟。
HTTP/2 also introduces Server Push that allows a server to send desired data to a client that the server anticipates the client will need in the future. Thus, HTTP/2 provides enhanced security, speed, and usability.
HTTP/2 还引入了 服务器推送,允许服务器将所需数据发送到服务器预期客户端将来需要的客户端。 因此,HTTP/2 提供增强的安全性,速度和可用性。
HTTP/2 uses the same URI scheme and shares the same default HTTP ports as of HTTP/1.1.
HTTP/2 使用相同的 URI 方案,并共享与 HTTP/1.1 相同的默认 HTTP 端口。
All communication is performed over a single TCP connection that can carry any number of bidirectional streams. Each stream has a unique identifier and optional priority information that is used to carry bidirectional messages. The frame is the unit of communication and there are several types of frames such as HEADER, DATA, and SETTINGS. For request and response communication, HEADER and DATA frames are primarily being used.
所有通信都通过单个 TCP 连接执行,该连接可以承载任意数量的 双向流。每个流都有唯一的标识符和可选的优先级信息,用于携带双向消息。帧是通信单元,有几种类型的帧,如 HEADER、DATA 和 SETTINGS。 对于请求和响应通信,主要使用 HEADER 和 DATA 帧。
Key benefits of HTTP/2
HTTP/2 的主要优点
Multiplexing
Unlike in HTTP/1.1 where each transfer has to wait till other transfers complete, in HTTP/2, multiple requests are allowed at the same time on the same connection.
与 HTTP/1.1 中的情况不同,其中每个传输必须等到其他传输完成,在 HTTP/2 中,在同一连接上同时允许多个请求。
In HTTP/1.x, only one response can be delivered at a time per connection, and if the client wants to make multiple parallel requests, then multiple TCP connections must be used. This also results in head-of-line-blocking and inefficient use of underlying TCP connection.
在 HTTP/1.x 中,每个连接一次只能传递一个响应,如果客户端想要进行多个并行请求,则必须使用多个 TCP 连接。 这也会导致线头阻塞和底层 TCP 连接的低效使用。
HTTP/2 overcomes these limitations by using the new binary framing layer ( where all HTTP/2 communication is split into smaller messages and frames and each of them is encoded in binary format so that both the client and server must use the new binary encoding mechanism in order to understand each other. Thus, an HTTP/1.x client will not understand an HTTP/2 only server and vice versa. ) by allowing the client and server to break down a message into independent frames, interleave them and reassemble them on the other end.
HTTP/2 通过使用新的二进制成帧层克服了这些限制(其中所有 HTTP/2 通信被分成更小的消息和帧,并且每个都以二进制格式编码,因此客户端和服务器都必须使用新的二进制编码机制因此,HTTP/1.x 客户端将无法理解仅 HTTP/2 服务器,反之亦然。)允许客户端和服务器将消息分解为独立的帧,交错并重新组合它们在另一端。
For example,
例如,
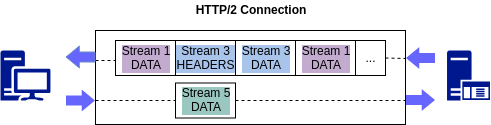
The above diagram illustrates multiple streams within the same connection. The client is transmitting a DATA frame over stream 5 to the server, while the server is transmitting an interleaved sequence of frames to the client over stream 1 and 3.
上图说明了同一连接中的多个流。 客户端通过流 5 将 DATA 帧发送到服务器,而服务器通过流 1 和 3 将交错的帧序列发送到客户端。
This also enables several performance benefits such as remove unnecessary HTTP/1/x workarounds in concatenated files, image sprites and domain sharding ( for further read refer: Optimizing for HTTP/1.x ), reduce the page load time by removing unnecessary latency and improving the utilization of available network capacity.
这还可以带来一些性能优势,例如在连接文件,图像精灵和域分片中删除不必要的 HTTP/1/x 变通方法( 有关进一步阅读,请参阅: 优化 HTTP/1.x),通过消除不必要的延迟并提高可用网络容量的利用率来减少页面加载时间。
Header compression
标头压缩
As web pages have grown to require dozens to hundreds of requests, the redundant header fields in these requests unnecessarily consume bandwidth, measurably increasing latency. So, HTTP/2 forces all HTTP headers to be sent in a compressed format, reducing the amount of information that needs to be exchanged between the client’s browser and the server whereas HTTP/1.1 does not provide any form of header compression.
随着网页变得需要数十到数百个请求,这些请求中的冗余头字段不必要地消耗带宽,可测量地增加了延迟。 因此,HTTP/2 强制所有 HTTP 标头以压缩格式发送,减少了客户端浏览器和服务器之间需要交换的信息量,而 HTTP/1.1 不提供任何形式的标头压缩。
The compression works on per connection basis. That is, all the streams in one connection share the same compressor. If the compressor realizes that it has sent a header before, it will not resend that header, instead just says ‘the same header as before’. So, some headers that never change like Host, Accept or Cookies will not get resent, and that will save a lot of bytes! 😃
压缩适用于每个连接。也就是说,一个连接中的所有流共享相同的压缩器。如果压缩器意识到它之前已经发送了一个报头,它将不会重新发送该报头,而只是说“与之前相同的报头”。 因此,一些永远不会像 Host、Accept 或 Cookies 那样改变的标题将不会被重新发送,这将节省大量的字节!
Server Push
服务器推送
Through the server push, additional resources can be sent to the client for future use, before the client even requests them.
通过服务器推送,可以在客户端甚至请求之前将其他资源发送到客户端以供将来使用。
Here, the server understands which resources the browser needs before the browser requests for them. Then the server will push these resources to the browser before it requests for them. This makes the entire process of retrieving all resources much faster.
在这里,服务器了解浏览器在浏览器请求之前需要哪些资源。 然后,服务器会在请求它们之前将这些资源推送到浏览器。 这使得检索所有资源的整个过程更快。
As an example when a browser requests a web page, a server responds with an HTML page and browser has to parse it and request again all embedded assets such as images, CSS and JavaScript files. In HTTP/2, using the server push concept a server can be configured to send all required assets according to a client’s request before the client requests them explicitly.
作为浏览器请求网页的示例,服务器响应 HTML 页面,浏览器必须解析它并再次请求所有嵌入的资源,例如图像,CSS 和 JavaScript 文件。 在 HTTP/2 中,使用服务器推送概念,可以将服务器配置为在客户端明确请求之前根据客户端的请求发送所有必需的资产。
Stream Priority
流的优先级
While multiplexing enables sending multiple requests concurrently, stream priority enables you to define which response should come first. I.e. it helps you to define the importance of one stream relative to the other streams on the same connection via weight and dependency associated with each stream. As a result, we can optimize the resource usage via controlling the allocation of CPU, memory, bandwidth and many other resources while ensuring the delivery of high priority responses to the client.
虽然多路复用可以同时发送多个请求,但流优先级使您可以定义应该首先响应的响应。 也就是说,它可以帮助您通过与每个流关联的权重和依赖关系来定义一个流相对于同一连接上的其他流的重要性。 因此,我们可以通过控制 CPU,内存,带宽和许多其他资源的分配来优化资源使用,同时确保向客户端传递高优先级响应。
Flow control
流量控制
This is introduced to prevent any destructive interference on streams with each other that are in the same connection that might have caused as a result of multiplexing which introduces contention over use of the TCP connection causing blocked streams. Flow control is used for both individual streams and for the connection as a whole.
引入这是为了防止对由于多路复用而可能导致的相同连接的流相互之间的任何破坏性干扰,这引起了对使用 TCP 连接导致阻塞流的争用。 流量控制用于单个流和整个连接。
Error handling
错误处理
HTTP/2 handles two classes of errors.
HTTP/2 处理两类错误
Connection error — any error that prevents further processing of the frame layer or corrupts any connection state.
Stream error — an error related to a specific stream that does not affect the processing of other streams.
连接错误 — 任何阻止进一步处理帧层或破坏任何连接状态的错误。
流错误 — 与特定流相关的错误,不会影响其他流的处理。
I will be talking on How to Write an HTTP/2 Service and a Client in my next story 😊
我将在下一个故事中讨论如何编写 HTTP/2 服务和客户端😊
Mar 11,2019 (2019-03-11)
author: Varuni Punchihewa
link: https://blog.usejournal.com/what-is-http-2-380d277d208c